Historical Timeline
1966

- National Academy of Sciences – National Research Council publishes a report titled Accidental Death and Disability: The Neglected Disease of Modern Society , which recommends the use of pilot programs to determine the efficacy of providing physician-staffed ambulances for care.
- Highway Safety Act of 1966 establishes national standards for inspections of used emergency services vehicles.
- National Traffic and Motor Vehicle Safety Act of 1966 specifies ambulance design and construction.
1967
- Dr. Frank Pantridge from Belfast, Ireland publishes the first study defining a Mobile Coronary Care Unit.
1969
 Dr. Walter Graf begins a Mobile Coronary Care Unit program at Daniel Freeman Hospital in Inglewood-Centinela. The “Heart Car,” donated by McCormick Ambulance and equipped with a cardiac monitor, defibrillator and radio communication equipment begins service.
Dr. Walter Graf begins a Mobile Coronary Care Unit program at Daniel Freeman Hospital in Inglewood-Centinela. The “Heart Car,” donated by McCormick Ambulance and equipped with a cardiac monitor, defibrillator and radio communication equipment begins service.- Board of Supervisors meet with community leaders and decide to train fire department personnel as paramedics.
September 12
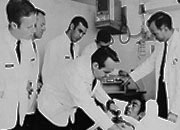 The first paramedic class begins training at Harbor General Hospital under Dr. J. Michael Criley and Critical Care Unit nurse Carol Bebout)
The first paramedic class begins training at Harbor General Hospital under Dr. J. Michael Criley and Critical Care Unit nurse Carol Bebout)
December 8

- The first LA County Fire rescue unit, Squad 59, officially goes into service. It is based on the grounds of Harbor General Hospital and is manned by two newly trained paramedics on each shift.
- Work begins on a state bill to allow paramedics to provide advanced medical life support without the direct supervision of a nurse or physician. It is introduced to both houses of the State by Senator James Wedworth and Assemblyman Larry Townsend.
1970
July 14

- The Wedworth-Townsend Paramedic Act is signed into law by Governor Ronald Reagan. California becomes the first state to adopt legislation permitting paramedics to provide advanced medical life support.
September

- The first paramedics graduate from the Paramedic Training Institute.
1971
May 11

- TV producer Robert Cinader becomes interested in developing new series regarding rescue for NBC and visits Los Angeles County Fire Station 7 and Station 36
1972
January

- The TV series “Emergency!” is first televised. The series raises public awareness of the paramedic program throughout the country
1973
- The Emergency Medical Services Systems Act of 1973 is signed into law, establishing federal grant funding for EMS systems.
1974
- Dr. Ronald Stewart, an emergency medicine physician, is placed in charge of the Paramedic Training Institute. He modifies the paramedic curriculum and writes the first paramedic training manual.
Late 1970s
- Continuing education programs are put into place. Paramedics are now required to recertify through written and skills examinations.
Late 1979
- The EMS Commission is established by County Ordinance
- The Board of Supervisors adopts the Advanced Life Support (ALS) Unit Staffing Policy, which requires two licensed paramedics to staff any ALS Unit.
1980
November

- The Emergency Medical Service and Emergency Medical Care Personnel Act is signed into law, mandating state responsibility for emergency medical services by designation of a local EMS Agency.
- The Los Angeles County Board of Supervisor authorizes the Health Services to fill the role of EMS Agency and becomes responsible for the overall coordination of emergency services in LA County.
1983
December 15

- The first eight Level 1 trauma hospitals are designated and activated by the Board of Supervisors.
Late 1983
- The US Supreme Court rules that local governments granting monopolies would not be exempt from antitrust laws unless policies were clearly articulated.
1984
- The EMS Act is amended to allow local EMS Agencies to create exclusive operating areas for private EMS providers such as ambulance companies.
1984-1985

- Hospitals with the capability of handling specialized needs of children are designated as Emergency Departments Approved for Pediatric Critical Care Centers
Late 1980s
- Testing and certification of paramedics is transferred from the local counties to the state.
July 1994
- By statute, paramedic certification is changed to licensure and testing is eliminated from the relicensure process.
1995
- The Paramedic Training Institute becomes affiliated with EL Camino Community College District.
1997
March
- The EMS Agency designated the first 5 Sexual Assault Response Team (SART) Centers.
September
- Standing Field Treatment Protocols (SFTPs) were approved by the EMS Agency for implementation for Los Angeles Fire Department. SFTPs allowed paramedics to provide emergency life-saving treatment without contacting a paramedic base hospital.
2002
February
- The EMS Agency received the first year of federal grant funding to prepare hospitals to respond to disasters under the Hospital Preparedness Program.
2003
August
- Subsequent to the implementation of pediatric specific Title 22 trauma center requirements, the EMS Agency designated the first 5 Pediatric Medical Critical Care Centers.
2004
June
- The EMS Agency, under the Hospital Preparedness Program designates 11 hospitals as Disaster Resource Centers to coordinate disaster planning and preparedness activities in their geographical areas. The DRC program becomes the foundation of emergency preparedness activities for the healthcare community.
2006
December 1

- The first three STEMI Receiving Centers (SRCs) are designated by the EMS Agency
2007
June
- Purchased Mobile Medical System comprised of a 10 bed emergency department tractor/trailer and support vehicle and an 100 bed tent facility.
2009
April

- The first 10 Approved Stroke Centers were designated by the EMS Agency.
2012
February
- The EMS Agency implemented regionalized system of care to cardiac arrest patients who sustain a return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). Patients with ROSC were transported to the STEMI receiving centers for possible hypothermia or percutaneous coronary intervention.
2012
June 7

- The EMS Agency partnered with the American Heart Association, local hospitals, EMS Provider Agencies and other Southern California EMS Agencies to sponsor the inaugural SideWalk CPR day.
2014
December
- Designation of two Ebola Treatment Hospitals.
2017
December

- Comprehensive Stroke System approved by the Board of Supervisors with the first 10 Comprehensive Stroke Centers designated
2018
- Implementation of two-tiered stroke system
- Implementation of Provider Impression based Treatment Protocols
2019
- Implementation of ECMO Trial Study
- EMS 50th Anniversary Celebration
- Established the Innovation, Technology and Advancement Committee (ITAC)
2020
- The Pandemic – Vaccination, PPE and therapeutic distribution
2022
- Implementation of i-gel
2024
- Transitioned the EMS Data Repository module of the Trauma and Emergency Medicine Information System (TEMIS) to be compliant with the National EMS Information System (NEMSIS) and California EMS Information System (CEMSIS) Standards.
2025
- Designated the first Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (ECMO) Centers.