Medical Imaging & Nuclear Medicine
Department of Medical Imaging
The Department of Medical Imaging provides diagnostic imaging services for both inpatients and outpatients.
The types of services we provide include MRI, CT scans, nuclear medicine, ultrasounds, bone density studies, IR, and general radiology.
We make every effort to accommodate our patients and make them as comfortable as possible during their examination. We strive to take quality diagnostic images.
To schedule an appointment, or if you have questions about the services we provide, please contact Medical Imaging at (562) 385-7532.
Carleton Allen, M.D., Chairman
Pauline Winterhalter, Chief Radiologic Technologist
Rancho Los Amigos Bone Density
JPI Extension
R1039 Bone Density
(562) 385-7532
Monday-Wednesday- Friday – 8:00 am to 4:30 pm
On-Call services available for inpatients
What is a Bone Density scan?
A bone density scan, also known as a DEXA scan, is a type of low-dose x-ray test that measures calcium and other minerals in your bones. The measurement helps show the strength and thickness (known as bone density or mass) of your bones. A bone density test determines if you have osteoporosis — a disorder characterized by bones that are more fragile and more likely to break.
Other names: bone mineral density test, BMD test, DEXA scan, DXA; Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry
If you have any questions or concerns, please call Nicasio Manuel at (562) 385-6771.
Rancho Los Amigos CT
JPI Extension
R1056 CT Control, R1058 CT Scan Suite
(562) 385-7532
Monday thru Friday – 8:00 am to 12:00 am
On-Call services available for inpatients
What is a CT scan?
CT scan was first introduced in the 1970’s. Computed tomography is commonly referred to as a CT scan. A CT scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses a combination of x-rays and computer technology to produce images of the inside of the body. It shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, organs, and blood vessels. CT scans excel at defining bone and vascular problems such as complex fractures and narrowing of aneurysms of blood vessels. CT scans provide greater clarity and reveal more details than regular x-ray.
Using specialized equipment and expertise to create and interpret CT scans of the body, radiologist can more easily diagnose problems such as cancers, cardiovascular disease, infectious disease, appendicitis, trauma, and musculoskeletal disorders.
CT scans may be performed to help diagnose tumors, investigate internal bleeding, or check for other internal injuries or damage. CT can also be used for a tissue or fluid biopsy.
If you have any questions or concerns, please contact Mark Washington, CT Supervisor, at (562) 385-7542.
Rancho Los Amigos IR
JPI Extension
R1060 Interventional Suite
(562) 385-7532
Monday thru Friday – 8:00 am to 4:30 pm
What is IR?
Interventional radiologists specialize in minimally invasive techniques to treat many conditions that once required open surgery with a large incision. They use small, hollow tubes (catheters), miniature instruments and imaging guidance to directly access arteries and veins without making large incisions.
If you have any questions or concerns, please call Mark Washington, IR Supervisor, at (562) 385-7542.
Rancho Los Amigos MRI
JPI Extension, R1035
(562) 385-8008
Monday thru Friday – 7:00 am to 9:00 pm
On-Call services available for inpatients
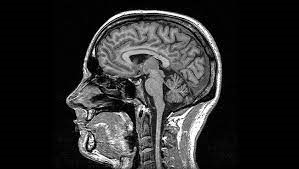
What is MRI?
An MRI is one of the newest and most technically elegant examinations ordered. Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, is a noninvasive medical imaging test that produces detailed images of almost every internal structure in the human body, including the organs, bones, muscles, and blood vessels. MRI scanners create detailed images of the body using a large magnet and radio waves to visualize the atoms of the body that may not be assessed adequately with other imaging methods such as x-ray, ultrasound, or computed tomography. The scanner can form images that provide a highly accurate roadmap of the human anatomy. No ionizing radiation is produced during an MRI exam, unlike X-rays. The Radiologist will provide an expert analysis of your images giving your physician important information in diagnosing your medical condition and planning a course of treatment.
Each scan can take between 30 minutes to an hour in general. Not everybody can have an MRI. If you have a pacemaker or automatic defibrillator, this test may not be right for, for your safety. This test is commonly ordered when a diagnostic solution cannot be obtained by other techniques.
MRI Safety and Screening:
Anyone coming near the MRI magnetic field should be screened for contraindications. A useful reference for determining MR compatibility is Dr. Frank Shellock’s Pocket Guide to MR Procedures and Metallic Objects. An excellent online reference maintained by Dr. Shellock, and colleagues is mrisafety.com. The best resource for assessing the MR conditionality of individual devices is the manufacturer’s website.
If you have any questions or concerns, please contact Fady Sadik, MRI Supervisor at (562) 385-7533.
Rancho Los Amigos Nuclear Medicine
JPI Extension
R1047 Spec/CT
(562) 385-7532
Monday thru Friday – 8:00 am to 4:30 pm
What is a Nuclear Medicine Scan?
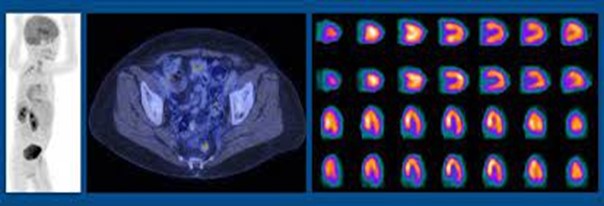
Nuclear medicine is a specialized area of radiology that uses very small amounts of radioactive substances to examine organ function and structure. It can also be used as a therapeutic approach to treat certain diseases.
Nuclear medicine scans provide information about various organ functions by imaging the concentration of specialty formulated radioactive chemical compounds selected parts of the body. These compounds, or radioisotopes, are administered to patients by trained technologists in small amounts to evaluate for functional abnormalities in bone, liver, lungs, heart, brain, kidneys and the endocrine system.
Nuclear medicine exams include: ventilation and perfusion (V/Q) scan for showing blood flow and air movement in the lungs; stress perfusion scan for assessing coronary artery blood flow and cardiac muscle damage; bone scan and PET scan for detecting the spread of cancer; liver, spleen, gallbladder, and kidney scans to evaluate organ function; thyroid scan to visualize activity of the thyroid gland; and scans of the gastrointestinal system to identify active bleeding sites.
Safety Concerns:
As with any radiologic procedure, pregnant women should consult with their physician before undergoing a nuclear medicine exam. Generally, nuclear medicine scans are not performed on pregnant women. Patients should also make sure their physician knows what medications they are taking and if they are a nursing mother before undergoing a nuclear medicine exam.
If you have any questions or concerns, please contact Mark Washington, Nuclear Medicine Supervisor at (562) 385-7542.
Rancho Los Amigos Ultrasound
JPI Extension
R1038 Ultrasound 1, R1040 Ultrasound 2, R1046 Ultrasound 3
(562) 385-7532
Monday thru Friday – 8:00 am to 4:30 pm
On-Call services available for inpatients
What is Ultrasound?
An ultrasound is an imaging test that uses high-frequency sound waves that travel from the ultrasound probe through human tissues and back to the transducer. This reflected sound is used by the computer to make pictures of organs, tissues, and other structures inside your body including blood vessels. It allows your health care provider to see into your body without surgery.
During an ultrasound, a healthcare provider passes a device called a transducer or probe over an area of your body or inside a body opening. The provider applies a thin layer of gel to your skin so that the ultrasound waves are transmitted from the transducer through the gel and into your body. The Radiologist will provide an expert analysis of your images giving your physician important information in diagnosing your medical condition and planning a course of treatment.
Ultrasound is also called ultrasonography or sonography. Ultrasound images may be called sonograms. There is no radiation dose associated with the ultrasound scan.
There are three main categories of ultrasound imaging, including:
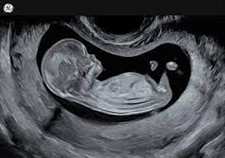
- Pregnancy ultrasound (prenatal ultrasound)
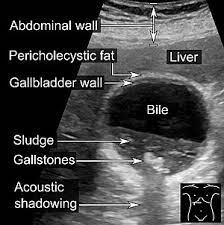
- Diagnostic ultrasound
- Ultrasound guidance for procedures
If you have any questions or concerns, please contact Mark Washington, Ultrasound Supervisor at (562) 385-7542.
Rancho Los Amigos X-Ray
JPI Extension
R1089 RM 1 & R1087 RM 2
(562) 385-7532
Monday thru Friday – 8:00 am to 4:30 pm
On-Call services available for inpatients
What is radiography?
Radiography is the grandfather of human imaging studies. Revolutionary refinements have taken place since 1895 when Wilhelm Roentgen first made an image of his wife’s hand and wedding ring.
Radiography is a procedure that uses a type of high-energy radiation called x-rays to take pictures of areas inside the body. X-rays pass through the body onto film or a computer, where the pictures are made. The tissues and organs usually appear in various shades of black and white because different tissues allow different amounts of the x-ray beams to pass through them. Radiography is used to diagnose or treat patients by recording images of the internal structure of the body to assess the presence or absence of disease, foreign objects, and structural damage or anomaly. Also called x-ray imaging.
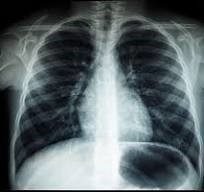
If you have any questions or concerns, please call Nicasio Manuel at (562) 385-6771.
Rancho Los Amigos Fluoroscopy
JPI Extension
RadFluoro 1 – R1083 & RadFluoro 2 – R1081
(562) 385-7532
Monday thru Friday – 8:00 am to 4:30 pm
On-Call services available for inpatients
What is Fluoroscopy?
Fluoroscopy is a study of moving body structures–similar to an X-ray “movie.” A continuous x-ray beam is passed through the body part being examined. The beam is transmitted to a TV-like monitor so that the body part and its motion can be seen in detail. Fluoroscopy, as an imaging tool, enables physicians to look at many body systems, including the skeletal, digestive, urinary, respiratory, and reproductive systems.
Fluoroscopy may be performed to evaluate specific areas of the body, including the bones, muscles, and joints, as well as solid organs, such as the heart, lung, or kidneys.
Fluoroscopy studies such as the upper gastrointestinal series are popular to evaluate patients with suspected gastroesophageal reflux and other problems such as swallowing difficulty.
Examples of studies performed: Video swallow, barium swallow, gastrografin, and Barium enema, to name a few.
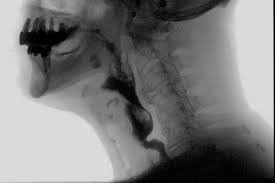
If you have any questions or concerns, please call Nicasio Manuel at (562) 385-6771.

